APCVD and LPCVD:
There is also another CVD method run at normal pressure. It is called atmospheric pressured CVD or AP-CVD. Here the temperature is relatively higher, in the range of 600 to 800 oC. In this method, a thick film can be formed quickly. However, there is risk of generating many dust particles and the film quality will be poorer. This method is used only in a few select cases.
Mass transfer control vs Reaction control: The following steps occur during CVD. First the reactant molecules diffuse through the boundary layer near gas-solid interface. Next the adsorb on the surface. In the third step, they diffuse on the surface. In the fourth step, they react with each other and the solid product is formed. Any gaseous byproduct formed may be adsorbed on the surface. Next, they desorb and diffuse outwards into the gas stream and get carried away.
When high temperatures are used, the reaction rate is very high and the rate of diffusion of the reactants through the boundary later decides the film growth rate. On the other hand, when the temperatures are lower, the mass transfer rate will decrease a bit, but the reaction rate will decrease a lot, and the surface reaction rate will decide the film growh rate. A plot of film growth rate vs inverse of temperature will appear as shown below.
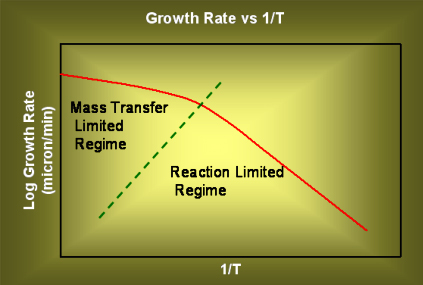
Figure 3.19. A qualitative plot of growth rate (in log scale) vs inverse of temperature.
The two different zones where diffusion is rate limiting and kinetics are rate limiting are marked.
APCVD is usually operated in high temperature regime, i.e. the film growth rate is diffusion controlled or mass transfer controlled. LPCVD is usually operated in relatively low temperatures and is reaction rate controlled.
We saw that sometimes the temperature has to be raised to anywhere between 150 to 1000 oC. For lower temperatures, normal heaters may be used. For high temperatures, heating lamps are used. The lamps enable us to start and stop the heating very quickly. This in turn results in good control of the deposition process.
Of late, organic gases containing metal atoms or ions are used in CVD. These are called metal-organic or MO-CVD. Based on a process that is similar to CVD, it is possible to create films of certain materials with exactly one atom thickness! This is called atomic layer deposition (ALD).
|