| |
2.6 Dissolution of Foreign Cations in an Oxide
2.6.1 Case-1: Parent oxide is MO and foreign oxide is Mf2O3.
The following scenarios are likely:
- Mf3+ occupies M2+ sites in MO giving rise to an extra positive charge on the metal site and a free electron according to the following defect reaction
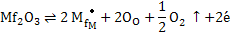 |
(i) |
- Alternatively for a metal deficient oxide MO, creates metal vacancies as
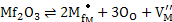 |
(ii) |
- For an oxygen deficient oxide, oxygen vacancies are compensated as
Reaction (iii) results in the reduction in vacancy concentration, while reactions (i) and (ii) result in increase in the electron concentration or metal vacancy concentration.
- Reaction (i), for a p-type conductor, can be alternatively expressed as following
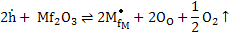 |
(iv) |
|