1.3 Packing of Atoms in Metals
- In solids, we consider atoms as hard incompressible spheres which can be packed in various forms. First we will see how atoms pack in metals.
- Atoms in many metals form closed packed structures either in the form of hexagonal closed packed structure or face-centered cubic structures. Some metals are a little loosely packed in the form of body-centered cubic structure. Very rarely atoms pack in metals in the form of simple cubic structure.
1.3.1 Simple Cubic Structure
- Simplest structure crystallographically but in the entire periodic table only polonium (Po) possesses this structure.
- Structure contains only one atom per unit-cell.
| Figure 1.15 Simple cubic structure |
1.3.2 Body Centered Cubic or BCC Structure
- Many metals like W, Fe (room temperature form) possess BCC structure.
- Contains 2 atoms per unit-cell
Figure 1.16 BCC Structure |
One of the important parameters of interest is packing factor, determining how loosly or densely a structure is packed by atoms.
Packing Factor: Volume of all atoms in one unit cell divided by Volume of one unit-cell
If r is the atomic radii in these structures, then
Packing Factor (Simple Cubic) = 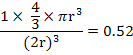
Packing Factor (BCC) = 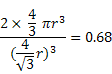
1.3.3
Closed Packed Structures
- Each atom has 12 nearest neighbours touching the atom to each other.
| Figure 1.17 Closed packing of atoms in FCC/HCP metals |
ABC ABC ABC . . . stacking leads to the formation of cubic closed packed (CCP) or face centered cubic (FCC) structure which has higher symmetry than other structures. The closed packed A, B, C planes are (111) planes in the structure.
AB AB AB . . . stacking leads to hexagonal closed packed (HCP) structure. The A or B planes are closed packed c-plane or (001) planes of hexagonal structure.
| Figure 1.18 FCC and HCP Structures |
Now you can work out yourself that packing factor of both FCC and HCP is 0.74.
|